What are the specific characteristics of the thoracic spine?
Symptoms and signs of thoracic osteochondrosis
- Chest pain that occurs as a result of staying in one position for a long time - manifested by sudden movements or strenuous physical activity;
- Deep inhaling and exhaling can cause pain and tightness in the mid-back;
- A stable pain syndrome occurs when the arm is raised and turned rapidly;
- Moderate pain was continuously observed in the scapula area;
- Certain parts of the body may become numb and desensitized;
- Unreasonable tingling or chills;
- Itching or burning in the legs and a drop in temperature relative to the rest of the body;
- The disease can cause side effects such as digestive disorders, intercostal neuralgia and problems in the reproductive area.

- Dorsago - severe pain, accompanied by stiffness and interference with normal breathing;
- Back Pain – Prolonged pain in the disc area.
Causes of thoracic osteochondrosis
- Pathology of the disc structure, including genetic predisposition to develop spinal disease;
- Intervertebral disc thinning and hernia;
- Decreased quality of cartilage tissue;
- Circulatory disorders that block blood flow to the spinal cord;
- The spine is subjected to unreasonable loads, leading to degeneration of muscle tissue, cartilage, or bone;
- Lack of vitamins and trace elements, mainly calcium;
- sustained physical activity;
- Sedentary lifestyle, working in front of a computer or driving;
- Spinal injuries and other injuries.

Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
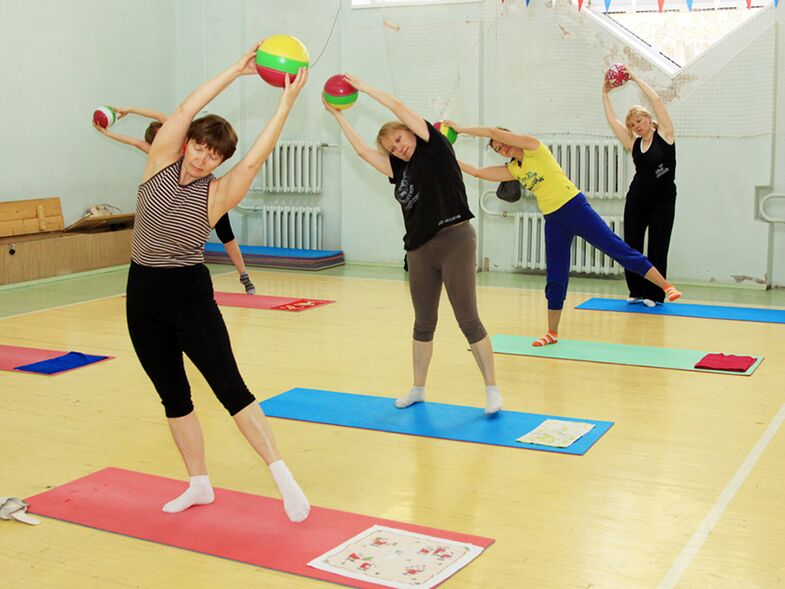
Exercise therapy for thoracic osteochondrosis

manual therapy
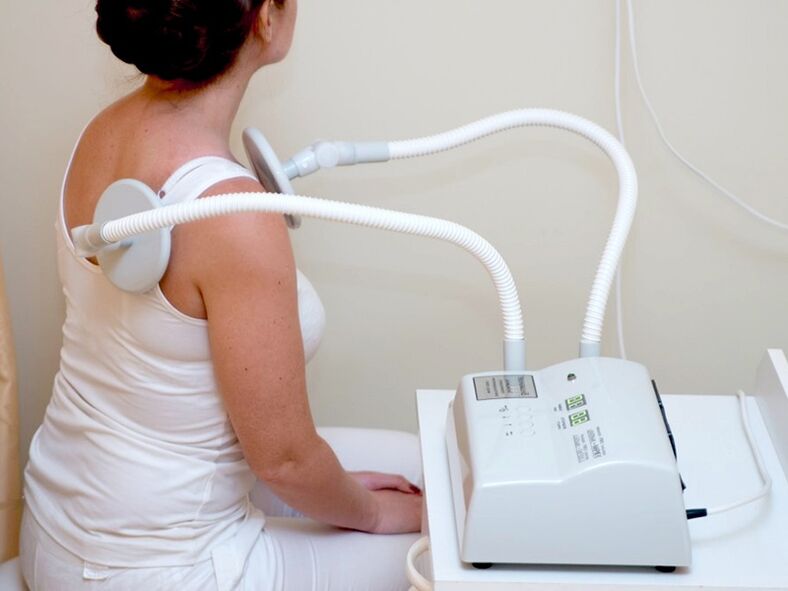
physiotherapy
- Shockwave therapy is the application of sound waves to the chest area. Improves metabolism, blood supply to affected areas, improves tissue repair and relieves pain;
- Decompression therapy - helps reduce the load on the spine and relieves spasms caused by the patient's own body weight;
- Electrotherapy – uses an electric field to heat tissue, delivering pulses to improve blood circulation and stimulate metabolism. Under the influence of electric current, drugs for the treatment of osteochondrosis are absorbed more efficiently;
- Ultraviolet light therapy – Quartz therapy enhances the production of vitamin D and can also help relieve pain and improve immune system function;
- Magnetic therapy - low-frequency electromagnetic fields improve the supply of useful substances to diseased areas, accelerate healing and improve blood flow;
- Laser Therapy – Laser can relieve cramps and pain, reduce inflammation, and stimulate tissue repair processes;
- Ultrasound – Ultrasonic vibrations help relieve pain, inflammation, and promote better absorption of medications.
medical treatement
- relieve pain;
- relieve inflammation;
- relax muscles;
- Improve local blood circulation;
- Restore metabolism;
- Enhance tissue regeneration.
folk remedies

- Soak horseradish leaves in boiling water and apply to affected areas - this can relieve the symptoms of osteochondrosis and regular treatment can prevent the condition from getting worse;
- Applying homemade cottage cheese with a few drops of vinegar on the body overnight can eliminate symptoms of osteochondrosis in the chest or neck;
- Rub a tincture of the leaves and flowers of the butterbur plant onto the affected area;
- Cool fresh rye flour cake slightly and apply it to sore areas to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Pour four cloves of garlic and three crushed lemons into boiling water and take one tablespoon at a time on an empty stomach. It cannot be used for gastritis and peptic ulcer;
- Replace regular tea with a decoction of bilberry leaves, one tablespoon per liter of boiling water;
- Horse sorrel, boil for ten minutes. Go away for a few hours and check into a couple of hotels three times a day. This is an effective treatment for osteochondrosis pain;
- Nettle juice. Mix one tablespoon of honey and ethanol in equal proportions three times a day for a week and a half.
What should I do if my condition gets worse?
- low temperature;
- Physical exercise;
- Overworked, constantly working hard;
- Training is too aggressive;
- Stress and other strains on the nervous system.

- Maintain bed rest and minimize physical activity and unnecessary exercise;
- maintain healthy eating habits;
- Follow all doctor's recommendations and take prescribed medications;
- Massage and rub the affected area;
- On the advice of a doctor - exercise therapy;
- Apply gels, ointments, and creams prescribed by your doctor to the chest and spinal area;
- Participate in a physical therapy program prescribed by your doctor.
Precaution
- Avoid lifting more than normal limits;
- Protects the spine from hypothermia;
- Take regular breaks to avoid overexertion;
- Make sure your posture is correct.
- Don't stay in the same position for long periods of time, especially if it's uncomfortable.